
Test BLACK with Turkesterone
Popular upgrades

Test BLACK with Turkesterone
OVERVIEW
FULLY DOSED TEST BOOSTER*
- Testosterone support*
- Features Maca and Tongkat Ali*
Description
Test BLACK™ was formulated with a single goal in mind - to maximize natural testosterone production and promote all things male within you.
Take a look at a few key ingredients in Test BLACK's™ open-label formula and see why it is an anabolic animal’s dream come true:
- Boron
- Maca Extract
- Turkesterone
- Fadogia
- Tongkat Ali (Eurycoma Longfolia)
Compare any other so-called “test booster” on the market to Test BLACK™ and you’ll see that it pales in comparison.
With Test BLACK™ you will leave weak at the door and total domination will ensue in the gym and on the field. Hands down, Test BLACK™ is sport’s nutrition's most advanced test booster….period!
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Supplement Facts
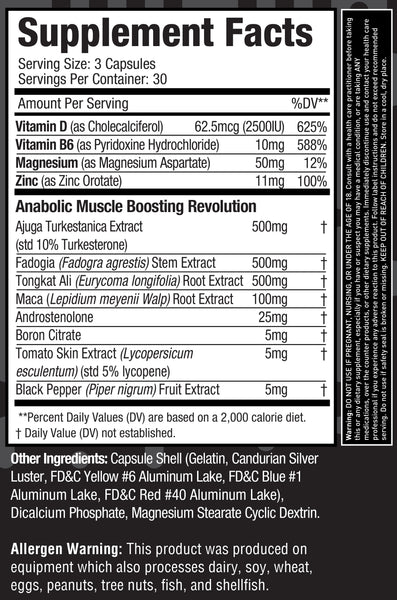
Ingredient Profile
Boron
Zinc
Magnesium
Vitamin B6
Vitamin D3
FAQs
Q: What is the best way to take Test BLACK?
A: As a dietary supplement, take one serving (3 capsules) in the morning with 8-10oz of water.
Q: What other MuscleSport products do you recommend stacking with Test BLACK?
A: We recommend stacking Test BLACK with Rhino Black, AminoREV, Lean Whey, and cycling with Life Shield for on-cycle and/or post-cycle therapy.
WARNING
California’s Proposition 65 entitles California consumers to special warnings.
WARNING: Cancer and Reproductive Harm - www.P65warnings.ca.gov/

